[ad_1]
Google today introduced a suite of updates for its online education tools whose adoption and further development have been accelerated by the pandemic, including Google Classroom, Google Meet and the next generation of G Suite for Education, now rebranded as Google Workspace for Education. In total, Google is promising more than 50 new features across its education products, with a focus on meeting educators’ and admins’ needs, in particular, in addition to those of the students.
When Google first introduced Google Classroom, it didn’t set out to create a Learning Management System (LMS), the company says. But during the COVID-19 pandemic, Google found that many educators had begun to use Classroom as the “hub” for their online learning activities. Today, the service is used by over 150 million students, teachers and school admins, up from just 40 million last year.
As a result of the pandemic-prompted adoption and user feedback, Google is introducing a range of new features for Classroom this year, some of which will be made available sooner than others.
To better cater to those who are using Classroom as the hub for online learning, a new marketplace of Classroom “add-ons” will allow teachers later this year to select their favorite edtech tools and content and assign them directly to students, without requiring extra log-ins. Admins will also be able to install these add-ons for other teachers in their domains.
Also later this year, admins will be able to populate classes in advance with Student Information System (SIS) roster syncing and, for select SIS customers, students’ grades from Classroom will be able to be exported directly to the SIS. Additional logging, including Classroom audit logs (to see things like student removals or who archived a class), as well as Classroom activity logs (to check on adoption and engagement) will be available soon.
When students attend in-person school, teachers can easily notice when a student is falling behind. A new set of Classroom tools aims to do the same for virtual learning, as well. With the new student engagement tracking feature, teachers will be able to see relevant stats about how students are interacting with Classroom, like which students submitted assignments on a given day or commented on a post, for example.
Image Credits: Google
Other tools will tackle the realities of working from home, where internet connections aren’t always reliable, or — for some low-income students — not available at all. With an updated Classroom Android app, students will be able to start their work offline, review assignments, open Drive attachments and write in Google Docs without an internet connection. The work will sync when a connection is again available. And when students upload assignments by taking a photo, new tools will allow students to combine photos into a single document, crop and rotate images and adjust the lighting.
Classroom will also gain support for rich text formatting — like bold, italics, underline and adding bullets across web, iOS and Android.

Image Credits: Google
Originality reports, which help to detect plagiarism, will be available soon in 15 languages, including English, Spanish, Portuguese, Norwegian, Swedish, French, Italian, Indonesian, Japanese, Finnish, German, Korean, Danish, Malaysian and Hindi.
And Google’s own free, introductory computer science curriculum, CS First, is immediately available in Classroom.
Beyond Classroom itself, Google Meet is also being updated with the needs of educators in mind.
One must-have new feature, rolling out over the next few weeks, is a “mute all” button to give control of the classroom back to teachers. In April, teachers will also be able to control when a student can unmute themselves, as well.
Image Credits: Google
Other moderation controls will roll out this year, too, including controls over who can join meetings, chat or share their screen from their iOS and Android devices. Policies over who can join video calls will be able to be set by admins in April, as well, enabling rules around student-to-student connections across districts, professional development opportunities for teachers, external speakers visiting a class and more. Students will also not be able to join Meets generated from Classroom until their teacher has arrived. Teachers, meanwhile, will be made meeting hosts so multiple teachers can share the load of managing classes.
Google Meet is adding engagement and inclusivity features for students, too. Students will be able to select emoji skin tones to represent them and react in class with emoji, which teachers will be able to control.
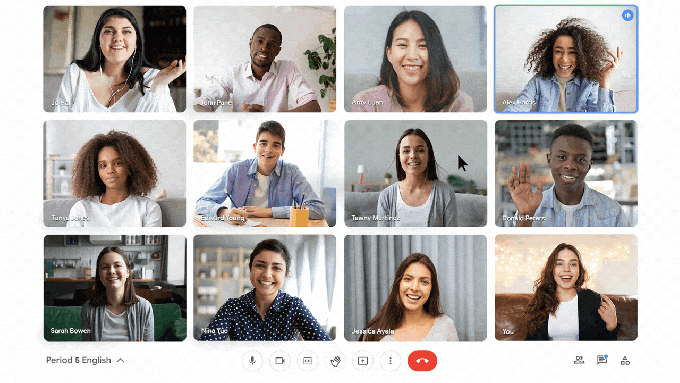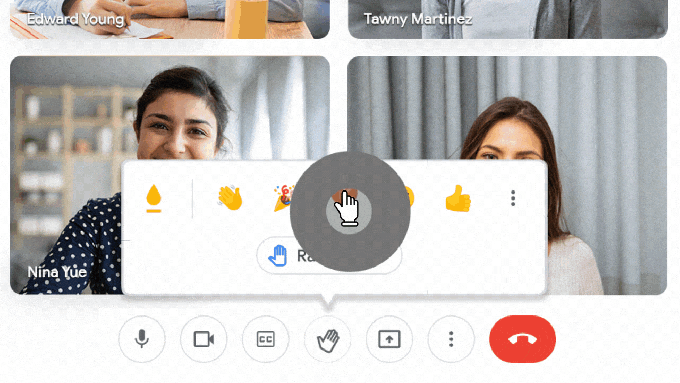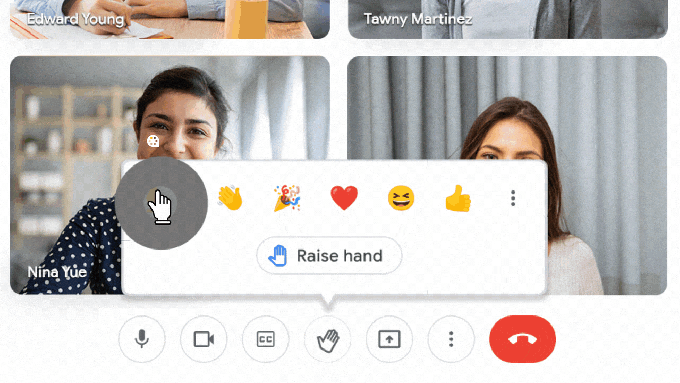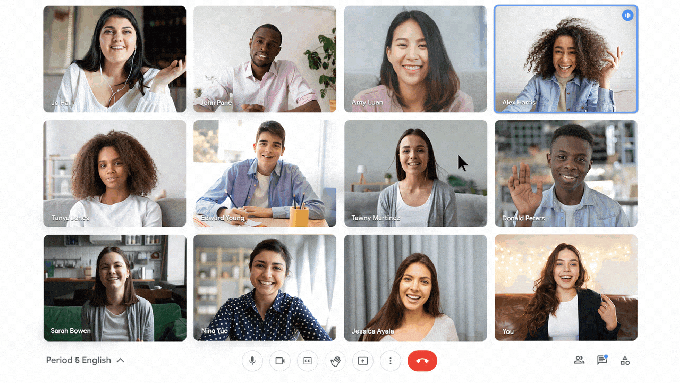
Image Credits: Google
Finally, Google’s “G Suite for Education,” which includes Classroom, Meet, Gmail, Calendar, Drive, Docs, Sheets, Slides and more, will be rebranded as Google Workspace for Education. The tools themselves, now used by 170 million students and educators globally, won’t change. But the set will be available in four editions instead of just two to better accommodate a wider variety of needs.
The free version will be rebranded Google Workspace for Education Fundamentals, and will remain largely the same. The paid version, meanwhile, will become available in three tiers: Google Workspace for Education Standard and Google Workspace for Education Plus, as well as the Teaching and Learning Upgrade, which can be added on to Fundamentals or Standard to provide video communication in Google Meet, and other Classroom tools, like originality reports.
Standard has everything in Fundamentals, in addition to enhanced security through Security Center, audit logs and advanced mobile management. Plus has everything in the three other versions, as well as advanced security and analytics, teaching and learning capabilities, and more.
Fundamentals and Plus are available today and the others will go live April 14, 2021. Those who already have G Suite for Enterprise for Education will be upgraded to Education Plus.
Related to these changes, the storage model will be updated to a new, pooled storage option that aims to better allocate storage resources across educational institutions. The new model offers schools and universities a baseline of 100 TB of pooled storage shared by all users, which goes into effect for current customers in July 2022, and will be effective for new customers in 2022. Google says less than 1% of institutions will be impacted by the updated model, whose baseline supports over 100 million documents or 8 million presentations or 400,000 hours of video, to give an idea of size.
The company plans several updates for its Google Workspace for Education product line in the weeks to come, including saved drafts in Google Forms (in Fundamentals) Google Meet meeting transcripts (in the Teaching and Learning Upgrade) and more.
Outside of software product updates, Google is launching over 40 new Chromebooks, including a set of “Always Connected” branded devices that have an LTE connectivity option built in. Chrome’s screen reader, ChromeVox, has also been improved with new tutorials, the ability to search ChromeVox menus and voice switching that automatically changes the screen reader’s voice based on the language of the text.
Parents, who are now participating in their child’s online learning in a number of ways, will be able to add their child’s Google Workspace for Education account to their child’s personal account with Family Link — Google’s parental control software. That means kids can still log into their school apps and accounts, while parents ensure they stay focused on learning by restricting other apps and overall device usage.
[ad_2]
Source link